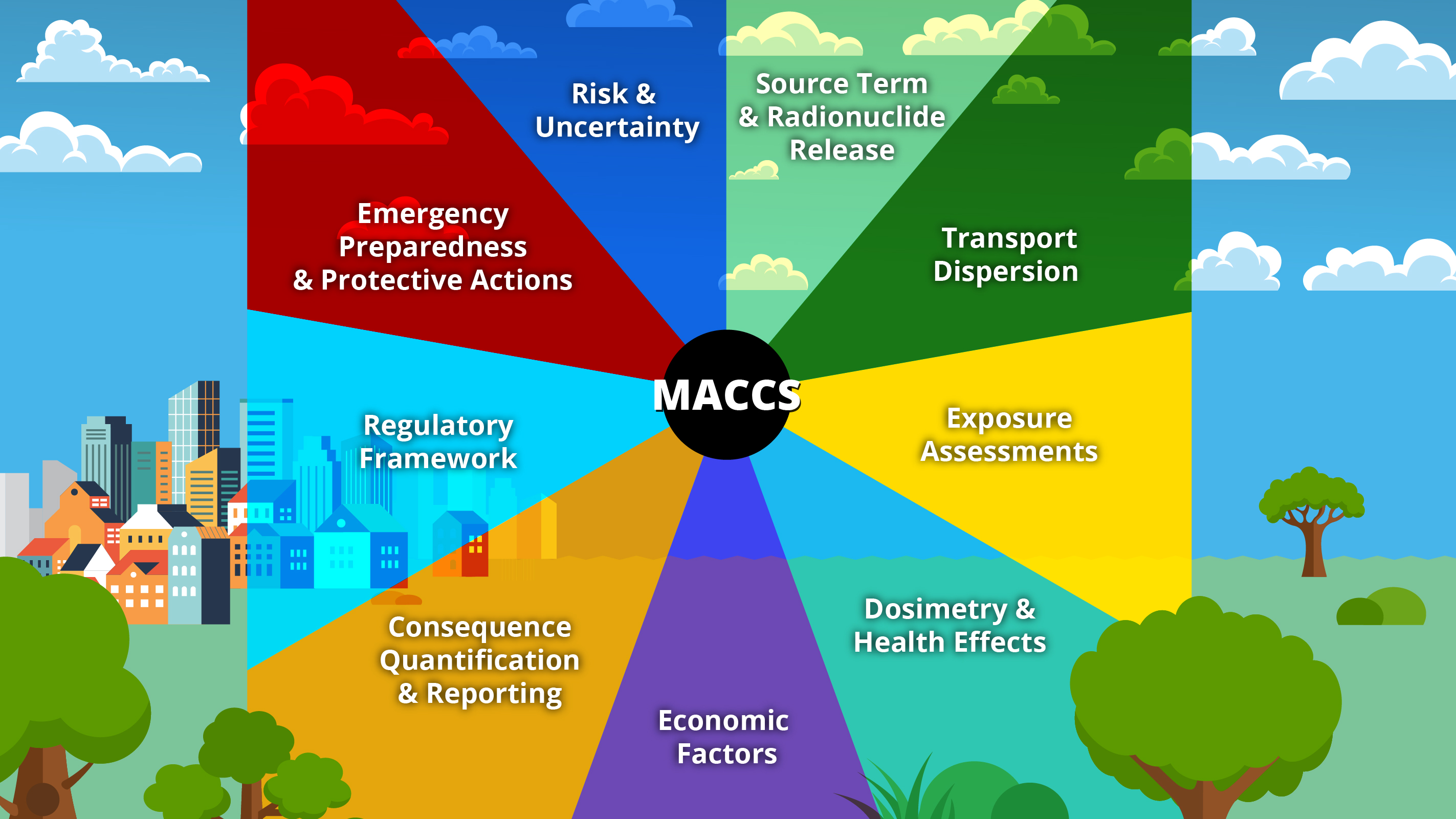
MACCS is a fully integrated, engineering-level computer code developed at
Sandia National Laboratories (SNL) for the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC). MACCS simulates the impact of severe
accidents at nuclear power plants (NPPs) and other nuclear facilities on the surrounding environment. As the only
code used by the NRC to support Level-3 a probabilistic risk assessments (PRAs), MACCS can use a site’s weather data
to determine hypothetical land contamination levels, doses to individuals, health effects and risks on populations
based on protective action recommendations, and economic losses resulting from a NPP accident. A list of references
can be located on the left-hand side of this webpage.
Release of MACCS Version 4.2
MACCS v4.2 is now available! Major enhancements for version 4.2 include the following:
-
License key: The "Product.key" is provided with the "WinMACCS 4.2.0 Setup.exe" file
and is no longer locked to a specific computer. This allows MACCS to run on multiple computers with the same license key,
including for cloud computing.
-
Cleanup criterion: A new dose-dependent cleanup criterion allows users to model the acceptable cleanup level
of contaminated areas. This now allows users to model decontamination in lightly contaminated, habitable areas in addition
to interdicted areas.
-
Dual dose criteria: Users now have the ability to model two relocation criteria in the long-term phase.
This allows users to model two dose criteria (e.g., 2 rem in the first year, 0.5 rem in the second year) to make a single
relocation decision, reflecting the US Environmental Protection Agency’s protective action guides.
-
Hotspot and normal relocation: Users now have two additional ways to model dose projections for early phase
hotspot and normal relocation, "TOTAL" and "AVOID". "TOTAL" evaluates the total dose from all air and ground concentrations
and "AVOID" evaluates the avoidable dose from ground pathways. These options are intended to mirror how decision-makers
would evaluate doses during a radiological emergency using Turbo-FRMAC.
-
RDEIM economic model: The new RDEIM model outputs have been updated to differentiate between gross domestic
product losses and offsetting recovery gains.
-
TEDE dose coefficients: MACCS now includes two sets of dose coefficients to estimate the effective dose,
"ICRP60ED" (based on ICRP-60) and "TEDE" (based on ICRP-30).
-
Radionuclide list: The limit to the number of radionuclides defined in MACCS has been changed from 150
to 999.
Release of MACCS-UI Version 5.0
MACCS-UI is completely updated code release for the MACCS interface to address software obsolescence
and other user interface improvements. Enhancements include the following:
- Modernize the software application with a modern system architecture, code design, and code reuse capabilities.
- Replace the Visual Basic framework with an Electron-based framework.
- Replace the Microsoft Access database with code data structures and the related code operations.
- Reduce code maintenance by deploying modular design principles and provide pathway for future MACCS improvements.
- Maintain the WinMACCS 4.2 functionality and backward compatibility with WinMACCS projects.
- Simplify and reduce the effort for completing input forms.
Additionally, MACCS will undergo a modernization effort in the next several years to update the underlying
programming language as well as expanding capabilities.
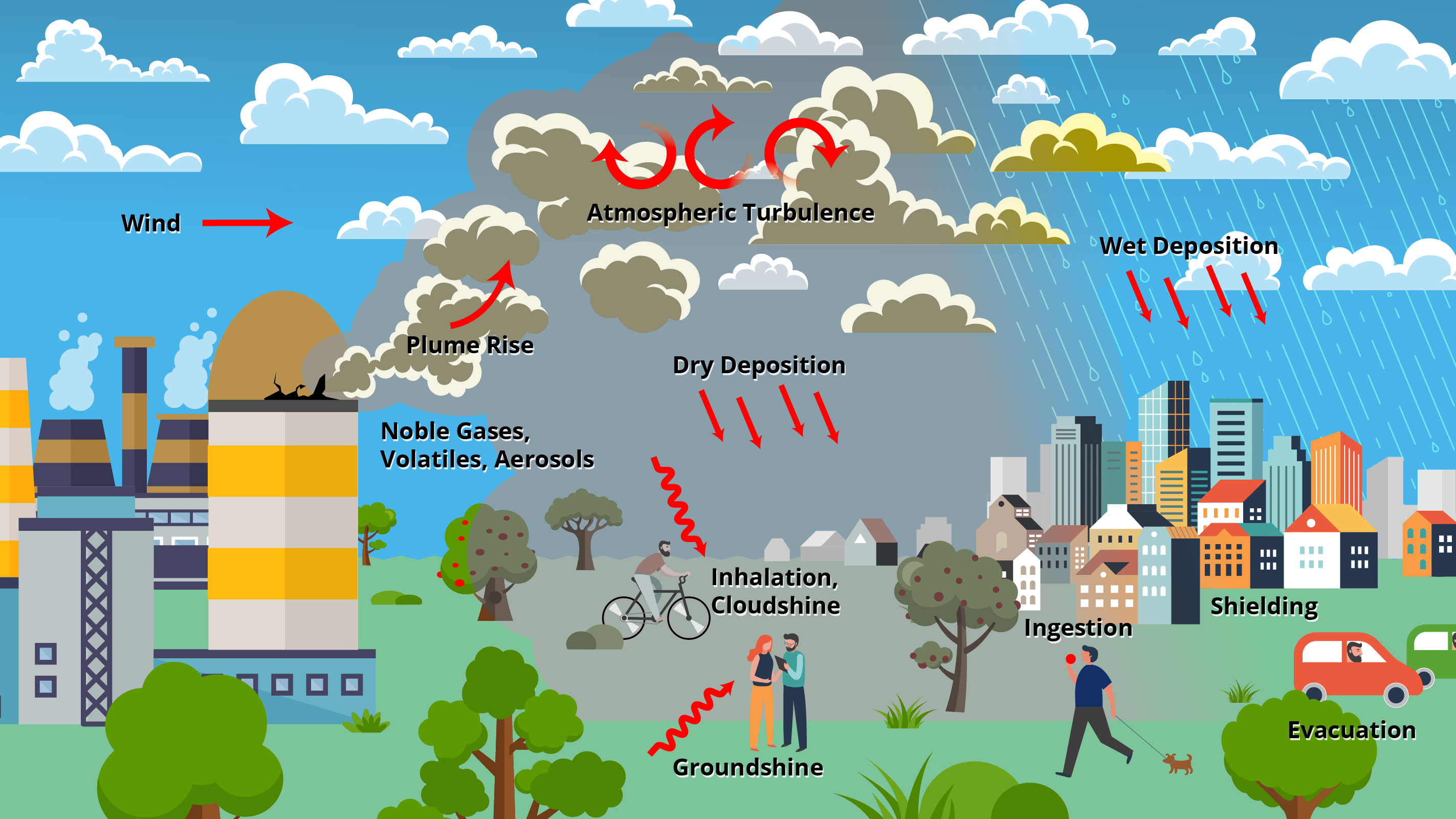
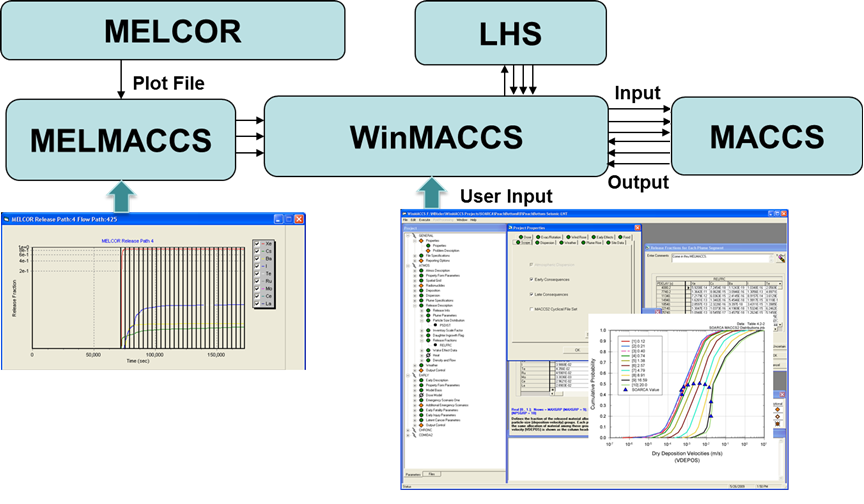
MACCS DATA FLOW
- User activates modules only as needed to determine results of interest
- Activated modules determine input files that are required
- Some required input files may be used as transmitted with MACCS (without user modification)
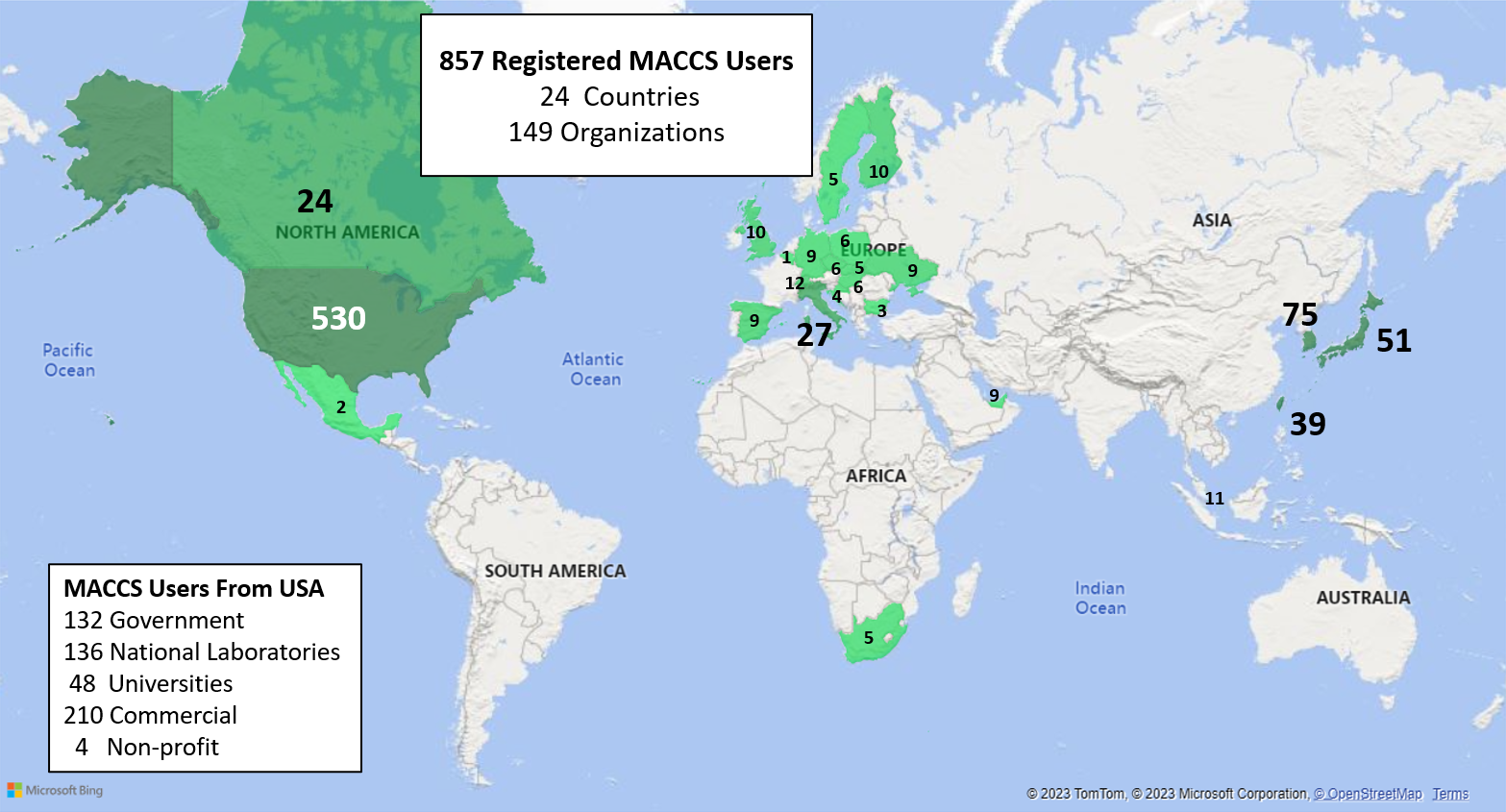
USER COMMUNITY
The MACCS user community includes both domestic and international users, to include the NRC, DOE, several research
organizations, nuclear industry licensees/applicants, and academic institutions. Primary uses of MACCS include
performing regulatory cost-benefit analysis, environmental analyses of Severe Accident Mitigation Alternatives
(SAMAs) and Severe Accident Mitigation Design Alternatives (SAMDAs), evaluations for emergency planning, Level 3
PRA studies, consequence studies, and other risk-informed activities.
INSTRUCTIONAL VIDEOS
REQUEST MACCS